This blog provides an in-depth look at the essential role of retinal screenings in managing diabetes and preventing one of its most serious complications, encouraging patients and providers alike to adopt these technologies into regular diabetic care practices.
I. Introduction
The Prevalence and Impact of Diabetic Retinopathy in Malaysia
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a leading cause of blindness among the working-age population in Malaysia and globally. The condition progresses from mild non-proliferative abnormalities, characterized by balloon-like swelling of the blood vessels in the retina, to more advanced proliferative diabetic retinopathy, where new blood vessels grow on the surface of the retina, which can lead to severe vision loss or blindness. The impact of DR is profound, affecting individuals’ quality of life, their ability to work, and contributing to the economic burden on the healthcare system.
Diabetic retinopathy remains one of the most significant complications associated with diabetes, particularly in Malaysia where the prevalence of diabetes is notably high. According to a recent study, diabetic retinopathy affects approximately 21% of known diabetic subjects in Malaysia, with men being slightly more affected than women. Ethnic background also plays a crucial role, influencing the prevalence and severity of the condition (Naveenkumar et al., 2014) [1]. This prevalence underscores the critical need for effective management strategies and highlights the importance of regular screening to prevent the progression that can lead to blindness.
Technological Advancements in Screening: OCT and DRS
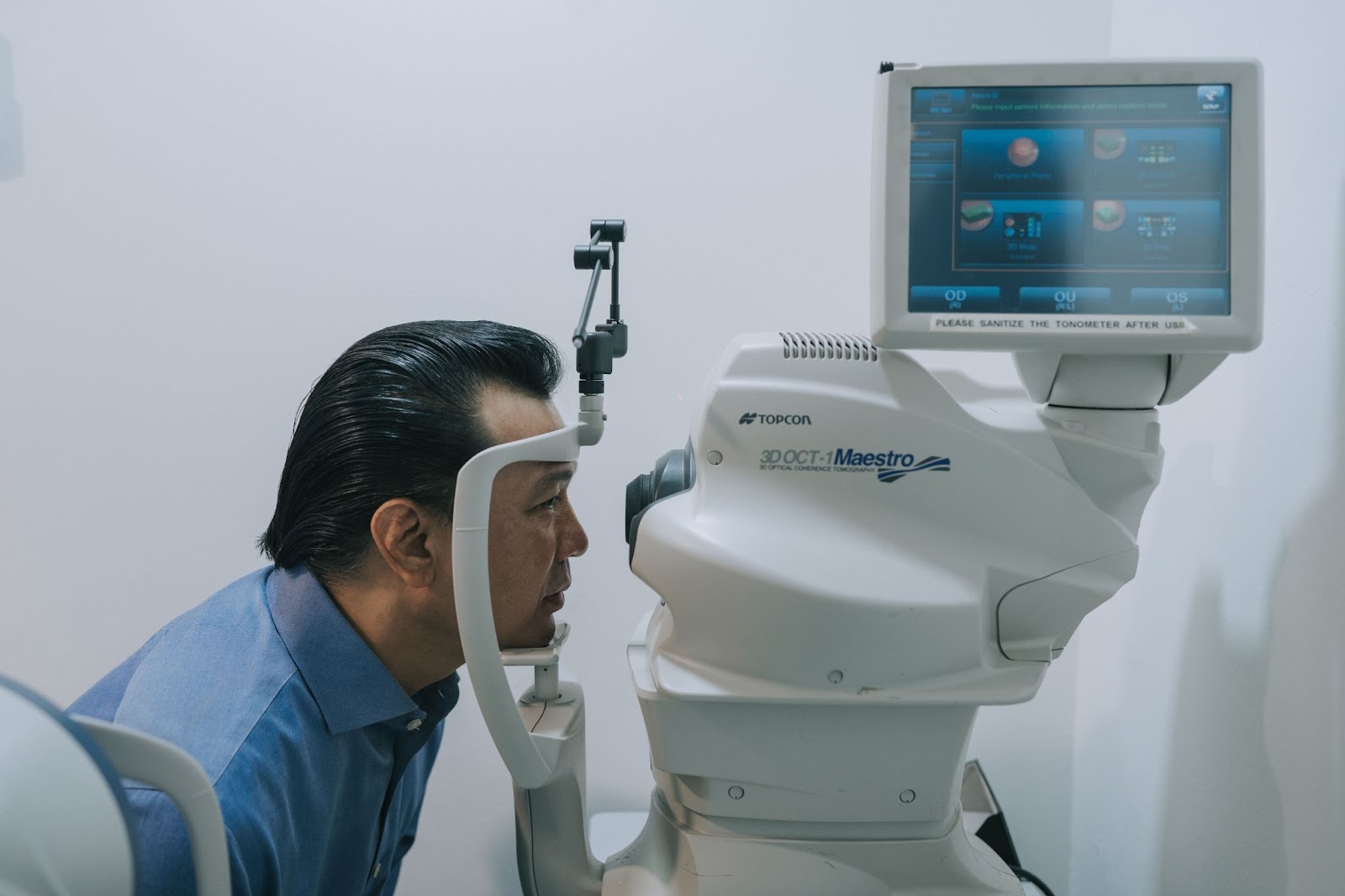
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) and Digital Retinal Screening (DRS) are at the forefront of technological advancements in eye care, offering non-invasive, quick methods to detect early signs of diabetic retinopathy. OCT, for instance, uses light waves to take cross-section pictures of the retina, revealing its detailed structure and any pathological changes.
A study conducted in Malaysia demonstrated that a computer-assisted diagnostic system using 3D OCT images achieved an impressive 94.74% accuracy in detecting diabetic retinopathy, showcasing the potential of advanced imaging technologies in improving diagnostic processes (Sharafeldeen et al., 20230 [2].
Importance of Regular Screening
The regular use of OCT and DRS not only aids in the early detection of diabetic retinopathy but also plays a crucial role in monitoring disease progression, allowing for timely interventions. The significance of these screenings cannot be overstated, especially considering the high rate of diabetes in Malaysia.
Regular screening enables earlier detection of subtle changes in the retina, which can be crucial for preventing severe outcomes and managing the condition effectively before it leads to irreversible damage.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the integration of OCT and DRS into regular diabetic care routines is vital for managing diabetic retinopathy in Malaysia. By leveraging these advanced imaging technologies, healthcare providers can offer better care, early interventions, and improved outcomes for diabetic patients, thus reducing the overall burden of diabetes on the healthcare system.
References
- [1] Naveenkumar, T., NagiReddy, T., & Radhakishan, N. “Diabetic eye screening in multi ethnic population of Malaysia: epidemiological risk factors for development of diabetic retinopathy.” International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences, 2014. [https://dx.doi.org/10.5455/2320-6012.IJRMS201408069].
- [2] Sharafeldeen, A., Mahmoud, A. M., ElTanboly, A., et al. “Diabetic Retinopathy Detection Using 3D OCT Features.” IEEE Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, 2023. [https://dx.doi.org/10.1109/ISBI53787.2023.10230785].
II. Understanding OCT and DRS in Diabetic Retinopathy Screening
Technological Overview of OCT and DRS
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) and Digital Retinal Screening (DRS) are advanced imaging modalities that have revolutionized the detection and management of diabetic retinopathy.
OCT provides detailed cross-sectional images of the retina, allowing clinicians to observe subtle changes in retinal layers which are critical markers for early stages of diabetic retinopathy. DRS, using digital imaging technology, captures comprehensive photos of the retina, facilitating a broader screening process that helps in early detection and timely management of eye conditions.
Diagnostic Efficiency in Malaysian Context
In Malaysia, the integration of OCT and DRS in diabetic retinopathy screening has been instrumental in improving diagnostic accuracy.
Recent studies, including one by Sharafeldeen et al. (2023), indicate that the application of advanced OCT imaging combined with computer-assisted diagnostic systems can achieve high accuracy rates (approximately 94.74%) in detecting diabetic retinopathy, showcasing the effectiveness of these technologies in clinical settings (Sharafeldeen et al., 2023) [2].
Impact on Early Detection and Management
The early detection of diabetic retinopathy is crucial in preventing the progression to severe stages that can lead to blindness. The capability of OCT to detect early microvascular changes and the extensive reach of DRS in community healthcare settings significantly enhance the screening process.
This is particularly important in Malaysia, where the prevalence of diabetes is high and access to specialized healthcare may be limited in rural areas. These technologies ensure that a larger portion of the population can be screened effectively, leading to better patient outcomes.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the benefits, there are challenges in widespread implementation, such as the need for further training for healthcare providers on the usage of these technologies and the integration of these systems into existing healthcare infrastructure.
Future advancements are likely to focus on enhancing the portability and affordability of these technologies, making them more accessible to various healthcare settings across Malaysia.
Conclusion
The use of OCT and DRS in diabetic retinopathy screening represents a significant advancement in the management of diabetes-related eye diseases in Malaysia. By enabling early detection and facilitating ongoing monitoring, these technologies play a crucial role in preventing vision loss among diabetic patients.
References
- [2] Sharafeldeen, A., Mahmoud, A. M., ElTanboly, A., et al. “Diabetic Retinopathy Detection Using 3D OCT Features.” IEEE Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, 2023. [https://dx.doi.org/10.1109/ISBI53787.2023.10230785].
III. Impact of Diabetic Retinopathy
Epidemiology and Significance
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) continues to be a significant public health issue in Malaysia, where the prevalence of diabetes is notably high. This eye disease is a leading cause of blindness among adults due to diabetes. It is estimated that about one-third of people with diabetes develop some form of diabetic retinopathy over time, emphasizing the critical need for effective management and intervention strategies to combat this trend.
Technological Advancements in Screening and Diagnosis
The introduction and advancement of Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) and Digital Retinal Screening (DRS) have transformed the landscape of diabetic retinopathy diagnosis and management. These technologies enable the early detection of retinal changes before they progress to more severe stages. For instance, OCT can visualize and quantify microvascular changes in the retina that are indicative of early diabetic retinopathy, which is crucial for initiating timely treatment.
Role of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Recent advancements in AI have further enhanced the capabilities of OCT and DRS by improving the accuracy and efficiency of diabetic retinopathy screenings. In Malaysia, AI algorithms integrated with OCT imaging have shown potential in increasing screening throughput and accuracy, which is vital for early intervention and treatment planning. These AI-enhanced systems can analyze vast amounts of imaging data rapidly, providing critical insights that support ophthalmologists in making informed decisions about patient care (Suciu et al., 2023) [3].
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite these technological advancements, Malaysia faces challenges such as uneven access to screening facilities, particularly in rural and underserved areas. The ongoing development and deployment of portable and cost-effective screening devices that incorporate AI could significantly improve accessibility and ensure that individuals at risk of diabetic retinopathy receive timely and adequate care.
Conclusion
The integration of OCT, DRS, and AI into the healthcare system holds significant promise for the management of diabetic retinopathy in Malaysia. By enhancing screening and diagnostic processes, these technologies play a crucial role in preventing the progression of diabetic retinopathy and associated vision loss.
References
- [3] Suciu, Corina-Iuliana, et al. “Diabetic Macular Edema Optical Coherence Tomography Biomarkers Detected with EfficientNetV2B1 and ConvNeXt.” Diagnostics, vol. 14, no. 1, 2023, p. 76. MDPI, [https://dx.doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14010076].
IV. Advantages of Regular Retinal Screening
Critical Role of Regular Retinal Screening
Regular retinal screening is paramount in the management of diabetic retinopathy in Malaysia, a country with a high prevalence of diabetes. The importance of these screenings lies in their ability to detect early signs of retinal changes, allowing for interventions before significant vision loss occurs.
According to recent studies, regular screening using advanced imaging technologies like OCT and DRS can significantly reduce the progression of diabetic retinopathy, thereby preventing severe outcomes and potential blindness (Penha et al., 2023) [4].
Technological Advancements: OCT and DRS
OCT and DRS have revolutionized diabetic retinopathy screening by providing detailed images of the retina, allowing for the early detection of even mild forms of the disease.
These technologies enable healthcare providers to monitor retinal changes over time, facilitating timely interventions such as laser surgery or injectable medications before irreversible damage occurs. The integration of these technologies into routine diabetic care enhances the effectiveness of treatments and improves patient outcomes.
The Impact of AI on Screening Processes
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in retinal screening processes has further enhanced the capabilities of OCT and DRS. AI algorithms can analyze retinal images with high accuracy, speeding up the diagnosis process and reducing the workload on healthcare professionals.
Studies have shown that AI-enhanced screening tools demonstrate high sensitivity in detecting diabetic retinopathy, making them valuable assets in community and primary care settings where specialist resources may be limited (Whitestone et al., 2023) [5].
Benefits of Regular Screening
The regular implementation of retinal screenings in Malaysia has shown considerable benefits, including:
- Early detection and management of diabetic retinopathy, significantly reducing the risk of blindness.
- Enhanced patient monitoring, allowing for adjustments in treatment plans based on individual patient needs.
- Cost-effectiveness by reducing the need for more expensive treatments for advanced stages of diabetic retinopathy.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the advantages, challenges such as accessibility, awareness, and the cost of advanced screening technologies persist. Addressing these challenges through public health initiatives and incorporating portable and less expensive screening tools can increase the reach and frequency of screenings, especially in rural or underserved areas.
Conclusion
Regular retinal screening using OCT, DRS, and AI technologies plays an indispensable role in the management of diabetic retinopathy in Malaysia. These screenings are crucial for preventing severe visual impairments and enhancing the quality of life for individuals with diabetes.
References
- [4] Penha, F., et al. “Single Retinal Image for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening: Performance of a Handheld Device with Embedded Artificial Intelligence.” Journal of Retina-Vitreous, vol. 10, 2023. [https://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s40942-023-00477-6].
- [5] Whitestone, N., et al. “Feasibility and Acceptance of Artificial Intelligence-Based Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in Rwanda.” British Journal of Ophthalmology, 2023. [https://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjo-2022-322683].
V. Conclusion: Combating Diabetic Retinopathy in Malaysia
Final Reflections on Technological Advances
The integration of Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) and Digital Retinal Screening (DRS) has marked a significant advancement in the fight against diabetic retinopathy in Malaysia. These technologies are not merely tools for diagnosis; they represent a shift towards proactive, preventative eye care.
The ability of OCT and DRS to detect early changes in the retina is crucial for initiating treatments that can halt or even reverse the progression of diabetic retinopathy, significantly reducing the risk of blindness associated with diabetes.
Impact of Regular Screenings
As underscored by recent clinical studies, regular screenings are essential for effective disease management. They allow for the early detection of retinal changes, enabling timely intervention and ongoing monitoring of the disease’s progression. The sensitivity of these technologies ensures that even the mildest forms of retinopathy are detected early, offering a better prognosis for patients (Penha et al., 2023) [4].
Role of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
The advent of AI in diabetic retinopathy screening has transformed the landscape of retinal examinations. AI algorithms enhance the accuracy and efficiency of OCT and DRS, reducing the workload on healthcare providers and ensuring that screenings are accessible and reliable.
The integration of AI has been shown to improve patient outcomes by supporting the detection of diabetic retinopathy at stages when it is most treatable (Whitestone et al., 2023) [5].
Encouragement for Proactive Health Management
Individuals with diabetes are encouraged to engage actively with their healthcare providers to utilize these advanced screening options. Regular retinal screenings should be a cornerstone of diabetes management, helping to preserve vision and improve quality of life.
Healthcare systems need to prioritize access to these technologies, ensuring that all patients, regardless of their geographical location or economic status, can benefit from these advancements.
Call to Action
We urge all stakeholders, including healthcare providers, patients, and policymakers, to advocate for the widespread adoption of OCT and DRS screenings in routine diabetic care. It is through collective effort and the utilization of advanced technology that we can hope to mitigate the impact of diabetic retinopathy in Malaysia.
References
- [4] Penha, F., et al. “Single Retinal Image for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening: Performance of a Handheld Device with Embedded Artificial Intelligence.” Journal of Retina-Vitreous, vol. 10, 2023. [https://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s40942-023-00477-6].
- [5] Whitestone, N., et al. “Feasibility and Acceptance of Artificial Intelligence-Based Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in Rwanda.” British Journal of Ophthalmology, 2023. [https://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjo-2022-322683].
This Article is Medically Reviewed by Woon Pak Seong

Woon graduated as an optometrist in 1995. After working for 9 years for a chain store and an individual optometry practice, he started Vision Space in 2004 to bring the best in global practices of vision care to customers.
He believes in the principle of continuous improvement and excellence. He enjoys meeting people and encouraging them to enjoy life.
A believer in lifelong learning, Woon loves to give optical training and talks at conferences and fairs. He takes delight in reading journals, magazines and books on how to serve his customers better as well as improving the practice of optometry.
His passion is to help people see clearly, comfortably and maintain good eye health through screening for potential eye diseases.
His specialties include:
1. Solving complex vision problems to help customers see clearly.
2. Helping children slow down their shortsightedness.
3. Fitting special multifocal spectacle lenses.
A fun fact about Mr. Woon: He is a movie buff and enjoys good music and food.
Favourite Quote: “Live life to the fullest.”

